
just go.
just go.
What is VSAM?
SAM (Secure Access Module) is a plug-in format smart card that enhances the security and cryptography performance in payment terminals, such as validators, for EMV contactless cards.
The VSAM is the Virtualization SAM and, as it’s sibling for closed loop applications CL_SAM, extends the features above providing open-loop and closed-loop payments by embedding the secure transaction processing which gives more security for the system. The VSAM carries also the EMV kernel L2 optimized for Visa “On Line Deferred” transaction and also provides an interface with an EMV Level 1 certified contactless reader to perform all EMV transaction quickly and securely with easy implementation.
So it can add EMV contactless card technology on top of legacy, without changing the validator application software and the automatic fare collection system back office.
The VSAM EMV Kernel L2 can handle:
The VSAM is remotely updatable, not only on its internal tables but also on its software using a secure method for both.
Besides the EMV Kernel L2, the VSAM has the flexibility to support other EMV scheme kernels becoming a very powerful, secure and customizable product.

Why VSAM?
Trends
The use of banking cards and mobile payment such Apple Pay, Google Pay and Samsung Pay in addition to existing legacy cards is a reality for public transportation payment. That’s because it is more convenient for the user, more secure for the operator and reduce the usage of cash money.
This trend represents a migration of current proprietary solutions to more secure card technologies (for instance, from MIFARE Classic to CIPURSE or EMV), reducing the risks of fraud by the use of older technologies.
Challenges
To accomplish the addition of EMV contactless banking cards acceptance on existing automatic fare collection (AFC) systems and improve the security of the existing proprietary systems (legacy), the solution must:

Current validators
Current validators are, in most cases, based on proprietary hardware and software which has been developed to accomplish the only goal to enable closed loop card as only way of ticketing. So the flexibility is limited becoming a barrier for the transportation stakeholders to develop new or upgrade existing transport applications.
How VSAM works?
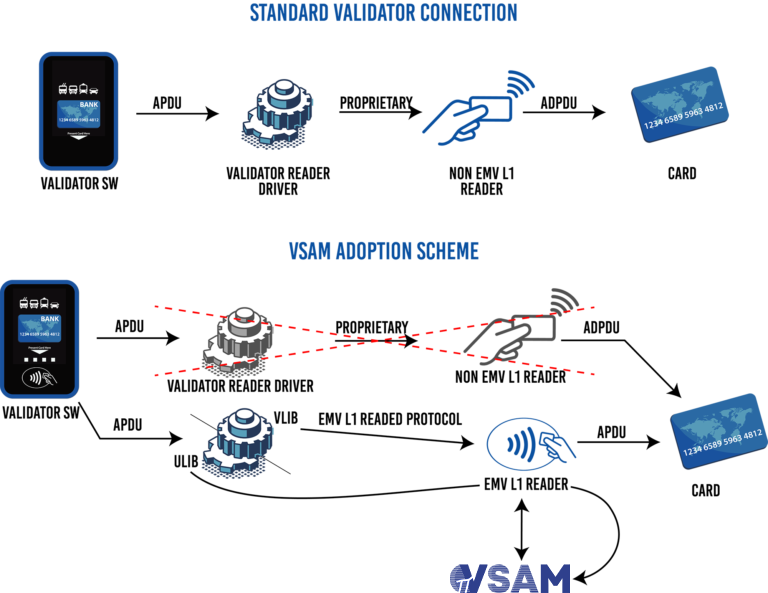
To overcome those challenges the VSAM uses the Interception concept that minimizes the change on current software. This alone represents more confidence on changes and less implementation effort.
The interception method works by delegating to the supplied library the card communication when it is not recognized by the standard validator application. I.e. The validator keeps searching for a card, when a closed loop one is found it treats as usual, but, when the card is not recognized, the validator uses the Virtualization Library (VLIB) that generates the APDUs to be sent to the card and get the returns performing all steps to execute the EMV transaction. Due to the security requirements, this operation must be done through an EMV level 1 certified reader which can be shared by the closed loop card or not.
The VLIB is a small library that bridges the card or media presented to the VSAM allowing the secure software inside of it to generate and process the APDUs performing the transaction.
The VLIB can also incorporate the ULIB that is the update library: This library is used to update the VSAM software and tables in a secure and transparent way for the host validator since it requires only a network connection to perform all operations in a secure way.
Methods
There are some approaches to implement the VSAM on legacy systems and they are described below

The S1 solution is the one where a new Level 2, Level 3 and MTT device with an EMV Level 1 reader is added to the system. This device shares the existing connection to send the authorization token to the closed loop host and can also activate a turnstile.
All the software components run inside this new device and no change is needed on the validator depending on the integration method.
In this mode, there will be one device to present the closed loop card and other for the open loop card.

The S2 solution replaces the reader inside the validator by an EMV L1 certified reader while the EMV L2, 3 and MTT are performed by the VSAM. To accomplish that, some libraries must be added to the validator’s code.
Both open loop and closed loop card are accepted in the same reader.
Solution 2+ (S2+)
The enhanced version of S2 differs by incorporating the libraries to the EMV L1 reader, and only a small footprint library must be added to the validator code. Thus, it makes the requirements for the validator simpler with no compromise on performance.
Both open loop and closed loop card are accepted in the same reader.

When the validator already has an EMV level 1 certified reader, only the addition of the VSAM is required and, as the S2, the libraries must be added to the validator’s code.
Both open loop and closed loop card are accepted in the same reader.
Solution 3+ (S3+)
In the scheme, the libraries are inserted in the reader with the VSAM, so the validator requirements are much simpler.

Since the VSAM is already EMVCo Level 2 certified, the combination with a EMVCo Level 1 reader enables a much simpler certification process, called regression test, that greatly accelerate the deployment which higher degree of confidence since the kernels are isolated.
A level 3 certification is requested for each acquirer/branding involved in the end-to-end solution.

At a glance
Visa Ready MTT model
The MTT model enables complete, multi-modal ticketing in environments where transaction speed is critical.
Features
Benefits

Where VSAM is being used?
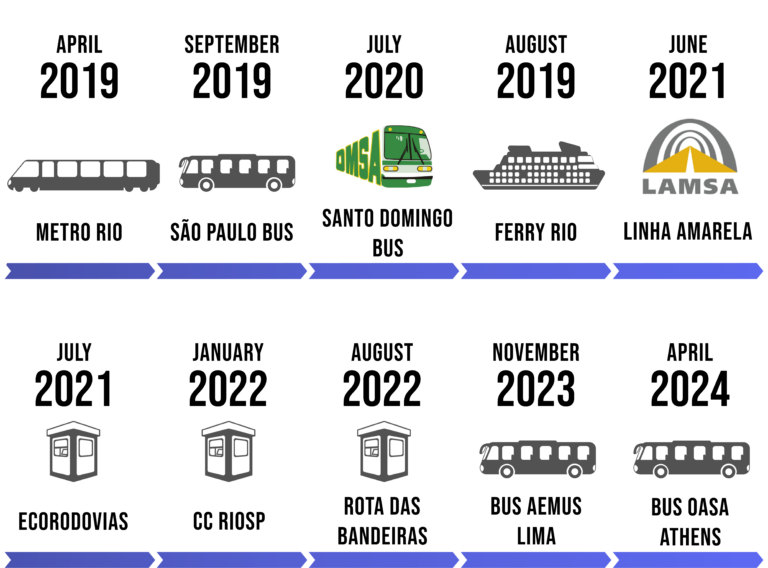
| MODAL | PTO/ CONCESSIONARY | LOCATION | PHASE | DATE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metro Bus Bus Ferry Boat Toll Toll Toll Toll Bus Bus | METRÔ RIO SPTRANS OMSA CCR BARCAS LINHA AMARELA ECORODOVIAS CCR RIOSP ROTA DAS BANDEIRAS BUS AEMUS LIMA BUS OASA ATHENS | RIO DE JANEIRO SÃO PAULO STO DOMINGO - D. REPUBLIC RIO DE JANEIRO RIO DE JANEIRO SÃO PAULO SÃO PAULO - RIO DE JANEIRO SÃO PAULO PERU GREECE | PRODUCTION POC PRODUCTION POC PRODUCTION PRODUCTION PRODUCTION PRODUCTION PRODUCTION PRODUCTION | APRIL/2019 SETEMBER/2019 JULY/2020 AUGUST/2020 JUNE/2021 JULY/2021 JANUARY/2022 AUGUST/2022 NOVEMBER/2023 APRIL/2024 |
Technical stuff

To add an EMV L1 reader:
Adaptations to accommodate EMV Level 1 contactless reader;
Alongside with the hardware components, the following libraries are needed for the proper operation:
VLIB – VSAM payment library
It is the library that exchanges the information between the VSAM and its host.
VLIB has 25 thousand lines of code and uses about 200kB of RAM memory.
RLIB – Reader library
It is the library that controls the reader itself managing its peripherals like LEDs, buzzer and etc.
RLIB has 5 thousand lines of code and uses about 20kB of RAM memory.
ULIB – Update library
It is library that manages the VSAM and reader software update.
ULIB has 250 lines of code and uses about 1kB of RAM memory.
VLIB lite
This is the light version of the VLIB, it is used on the “plus” solution where the other 3 libraries above are embedded into de reader. This library has four main functions:
- Provides a uniform interface between the reader and the host.
- Convert (if needed) the original reader protocol to the standardized one.
- Adapts the external TCP/IP communication interface to the VSAM, allowing the communication and name resolution. This can be done by using a pre-established TCP socket where the data in and out is managed by the VSAM.
- Gets date and time.
VLIB lite has from 200 to 500 lines of code depending on the need of protocol conversion and uses around 4kB of RAM.
In some cases, if necessary, it is possible to migrate part of the validator program to the VSAM in order to release memory and reach these software requirements.
The system also needs memory for storing data as described next. This memory can be allocated on the host or on the reader according to the availability.
DLM – Deny list memory.
Deny list stores the card identifiers that are no allowed to perform transactions. It is recommended at least 64MB that can store up to 1 million of entries and the system can handle few Gigabytes of memory if needed.
LLM – Log list memory.
This list store the transactions before the go on-line, in other words, the transactions performed off-line are stored in this memory and when the connectivity is present, they are uploaded. It is recommended at least 4MB for 1 thousand transactions and 64MB at maximum.
ELM – Event list memory.
This memory stores all the system events, like reboot, time adjustment. It is recommended 4MB for 32 thousand operations.
How to start
The VSAM SDK is the best way to start the development because it gives access to the source code, application examples on the reference hardware.
The hardware also is already working with EMV and can be demoed in 10 minutes. It is composed by an EMV adaptor with an embedded EMV L1 reader with a VSAM installed and it is supplied with 4 other full sized plug-in VSAM.
The goal of the SDK, besides instant demo, is provide comparison hardware to facilitate the implementation and performance comparison with other devices that can be tested with the VSAM supplied.
The VSAM SDK is a complete quick start method for the VSAM development and can be acquired here.

Technical characteristics
The SDK comes with access credentials to the valuable resources as:
- VLIB source code (C, Java and Node)
-
Protocol documentation of the VSAM to host
communication and VSAM to EMV reader - Source code of the implementation software
Besides the documentation, it includes:
- 16-hour e-mail support for up to 90 days after SDK receiving
- Access to special prices on buying other devices from the ecosystem as well BackOffice hours which are not available before the SDK acquisition and register.
- Full source code of the Nano EMV A2 demo application
Find out more
About
Planeta Informática has been an industry-leading SAM provider since 2003 and a leading provider of security elements and solutions to automated fare collection since 2002 with more than 200,000 SAM devices currently deployed, supporting 30 million users per day across South America.
Planeta was created in 1991 by a group of researchers from the telecommunication area and focuses on developing products based on open standards. We believe the use of open standards is the only way to have an interoperable product and, at same time, a competitive behavior.
Among their services, Planeta provides consultancy on AFC payment, recharge network and products as SAM devices, reference designs for secure devices and payment modules for companies all over Brazil, Latin America and Europe. Back in 2018, Planeta started collaborating with Visa to accelerate the open loop acceptance on mobility applications.


